first aid cpr aed participant’s manual pdf
This manual serves as a comprehensive guide‚ equipping participants with essential first aid‚ CPR‚ and AED skills to respond confidently in emergencies. It outlines structured lessons‚ step-by-step techniques‚ and practical scenarios to ensure preparedness and competence in saving lives. Designed for diverse learners‚ the manual emphasizes hands-on training and real-world application‚ making it an indispensable resource for anyone seeking to master life-saving interventions.
Overview of the Manual
The First Aid CPR AED Participants Manual offers a structured approach to learning life-saving techniques. It covers recognizing emergencies‚ performing CPR‚ using an AED‚ and providing care for injuries. The manual is comprehensive‚ user-friendly‚ and designed to build confidence in handling real-life emergencies. Participants gain practical skills through clear instructions‚ illustrations‚ and scenarios‚ ensuring they are well-prepared to respond effectively in critical situations. Regular updates align with the latest guidelines‚ making it an essential resource for first aid training.
Key Components of the Manual
The manual includes detailed sections on first aid‚ CPR‚ and AED usage‚ supported by visual aids and step-by-step guides. It emphasizes hands-on practice‚ scenario-based learning‚ and quick reference materials. Participants also gain access to supplementary resources‚ such as checklists and assessment tools‚ to reinforce learning. The content is updated regularly to reflect the latest medical guidelines‚ ensuring participants receive accurate and effective training.
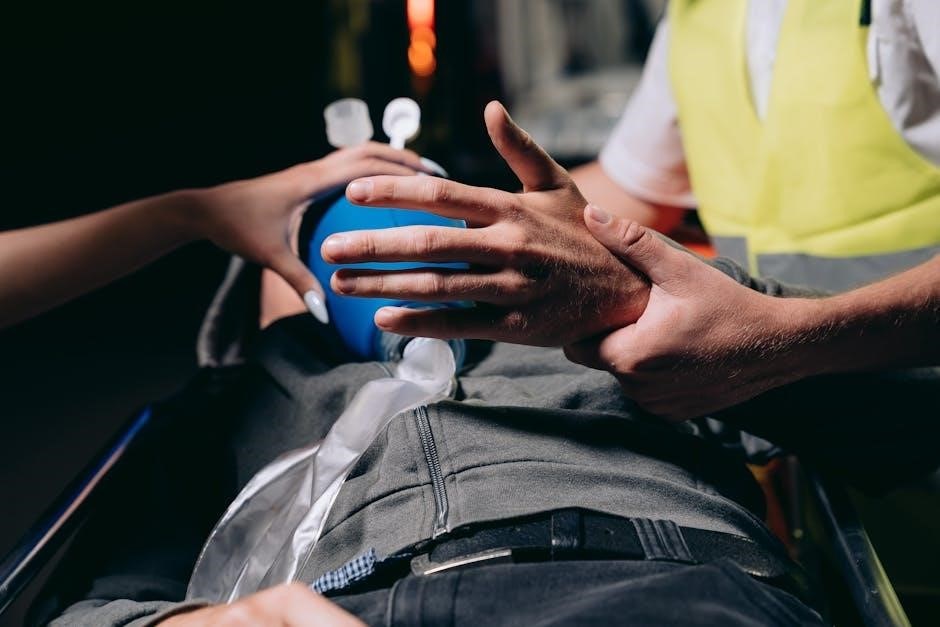
The Importance of First Aid and CPR Training
Empowering individuals to act decisively in emergencies‚ first aid and CPR training enables life-saving interventions‚ making a critical difference in outcomes and community safety.
Why First Aid and CPR Certification is Crucial
First aid and CPR certification provides individuals with the knowledge and confidence to act swiftly in emergencies‚ potentially saving lives. It ensures awareness of legal responsibilities and Good Samaritan protections‚ fostering a safer community. Certification also equips individuals with universal skills applicable in various emergency scenarios‚ making it a vital asset for personal and professional life. Timely intervention can significantly improve outcomes‚ emphasizing its importance.
Benefits of Learning First Aid and CPR Techniques
Learning first aid and CPR techniques empowers individuals to act confidently in emergencies‚ reducing panic and improving decision-making. These skills enable immediate assistance‚ potentially preventing minor injuries from escalating. They foster a safer environment‚ promoting community well-being and preparedness. Acquiring these techniques enhances personal and professional safety‚ ensuring timely and effective responses to life-threatening situations‚ ultimately contributing to better outcomes and saving lives.
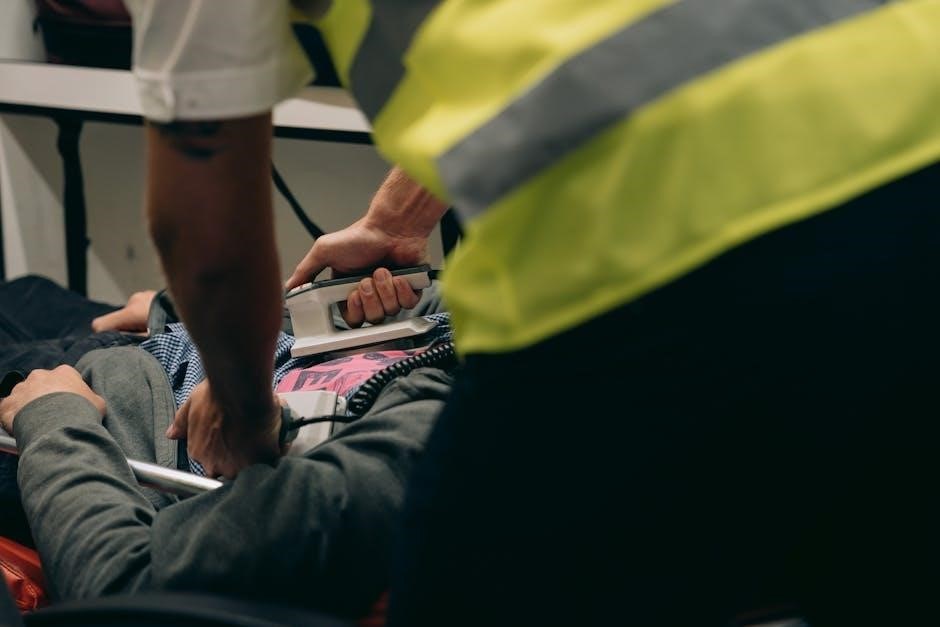

Roles and Responsibilities of a First Aid Provider
A first aid provider assesses emergencies‚ provides immediate care‚ and stabilizes conditions until professional help arrives‚ ensuring safety and administering techniques learned through certified training.
Understanding the Role of a First Aider
As a first aider‚ your primary role is to assess situations‚ provide immediate care‚ and stabilize individuals until professional medical help arrives. This involves recognizing emergencies‚ administering CPR‚ using an AED‚ and managing injuries or illnesses. Effective first aiders remain calm‚ act decisively‚ and prioritize the victim’s safety and well-being. Their actions can significantly impact outcomes‚ making proper training and confidence essential for saving lives and reducing suffering.
Legal and Ethical Responsibilities
First aid providers must act within the scope of their training and local laws. Good Samaritan laws protect individuals who provide aid in good faith without expectation of payment. Ethically‚ first aiders must respect patient autonomy‚ maintain confidentiality‚ and avoid actions that could cause harm. Documentation of care provided is often required for legal and accountability purposes. Understanding these responsibilities ensures compliance and protects both the provider and the patient.
Basic Life Support and CPR Techniques
Basic Life Support (BLS) focuses on maintaining circulation and breathing through high-quality CPR. It includes the chain of survival: recognition‚ activation‚ CPR‚ defibrillation‚ and advanced care. Proper BLS ensures timely interventions‚ minimizing delays in life-saving actions during cardiac emergencies.
The Chain of Survival
The Chain of Survival is a series of critical steps to maximize cardiac arrest survival: recognition‚ emergency call‚ CPR‚ defibrillation‚ and advanced care. Recognition involves identifying cardiac arrest and activating the emergency response system. Immediate CPR maintains blood circulation‚ while timely defibrillation restores a normal heartbeat. Advanced life support follows‚ ensuring the best outcomes. Each link in the chain is vital to saving lives effectively.
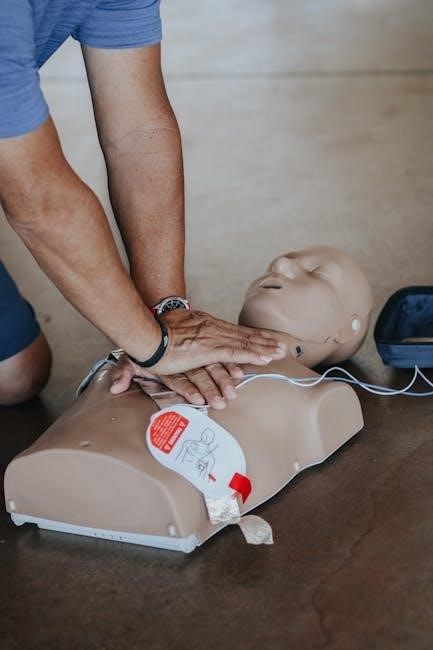
Step-by-Step CPR Process
Begin by assessing the victim’s responsiveness. Call 911 or your local emergency number immediately. Start CPR with 30 chest compressions at a rate of 100-120 per minute. Allow the chest to recoil fully between compressions. If trained‚ provide rescue breaths after every 30 compressions. Use an AED if available‚ following its prompts. Continue CPR until emergency medical personnel arrive or the victim regains consciousness.

Automated External Defibrillator (AED) Usage
Turn on the AED and follow voice prompts. Attach pads to the victim’s bare chest as shown. Deliver a shock if advised. Do not delay CPR.
What is an AED and How It Works
An Automated External Defibrillator (AED) is a portable device designed to restore a normal heart rhythm during sudden cardiac arrest. It analyzes the heart’s electrical activity‚ detects life-threatening arrhythmias‚ and delivers an electric shock to restart the heartbeat. Simple to use‚ AEDs provide voice or visual instructions‚ guiding responders through the process. They are essential in emergencies‚ significantly increasing survival chances when used promptly alongside CPR.
Proper Use of an AED in Emergency Situations
Turn on the AED and follow the voice prompts. Ensure the victim is unresponsive and not breathing. Place the pads on the bare chest as shown. Analyze the heart rhythm and deliver a shock if advised. Continue CPR after the shock‚ repeating the cycle until emergency services arrive. Always follow the device’s instructions for proper use in life-threatening situations.
Assessing Injuries and Providing Care
Ensure scene safety‚ assess the victim’s responsiveness‚ and check airway‚ breathing‚ and circulation. Provide care based on the injury or condition assessed.
Initial Assessment of the Victim
Begin by ensuring the scene is safe. Check the victim’s responsiveness by asking questions or tapping gently. Assess airway‚ breathing‚ and circulation (ABCs). Look for signs of injury‚ bleeding‚ or distress. Use gloves if available to protect against bodily fluids. Provide reassurance and position the victim appropriately‚ avoiding movement unless necessary for safety. This initial evaluation guides further care and interventions.
Signs of Serious Injuries or Conditions
Recognizing serious injuries or conditions is crucial for timely intervention. Look for unresponsiveness‚ difficulty breathing‚ or irregular breathing patterns. Severe bleeding‚ head trauma‚ or signs of shock (pale skin‚ rapid heartbeat) indicate critical situations. Chest pain‚ seizures‚ or loss of limb function also signal serious conditions. Burns‚ severe allergic reactions‚ or stroke symptoms (slurred speech‚ facial drooping) require immediate attention. Always prioritize professional medical care when these signs are present;

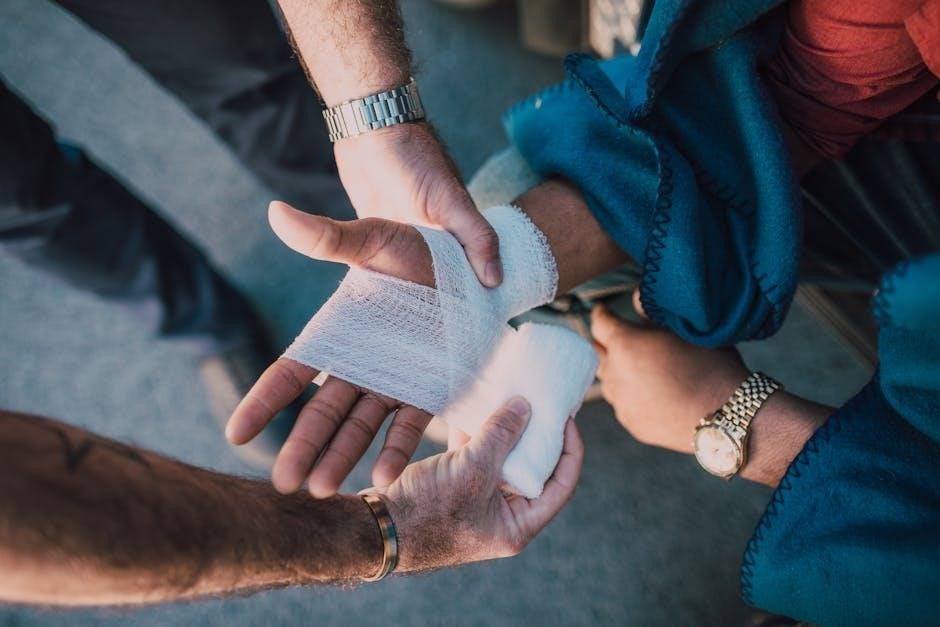
Handling Burns and Wounds
Properly assess burns by size‚ depth‚ and location. Cool burns with water‚ avoid ice‚ and cover with sterile dressings. For wounds‚ clean with saline‚ apply pressure to stop bleeding‚ and dress appropriately. Seek professional help for severe cases or signs of infection.
Types of Burns and Appropriate Care
Burns are classified into first‚ second‚ and third degrees based on severity. First-degree burns affect the outer skin layer‚ requiring cooling and topical creams. Second-degree burns extend to the underlying layer‚ needing similar care plus wound dressing. Third-degree burns penetrate deeply‚ necessitating immediate medical attention. Proper care involves cooling the burn‚ avoiding ice‚ and covering with sterile dressings to prevent infection. Timely intervention is crucial for recovery.
Managing Wounds and Preventing Infection
Proper wound care is essential to prevent infection and promote healing. Cleanse the wound with sterile water‚ pat dry‚ and apply antibiotic ointment. Cover with a sterile dressing‚ changing it daily or when wet/dirty. Monitor for signs of infection‚ such as redness‚ swelling‚ or pus. Seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen. Timely care reduces infection risk and supports recovery.

Emergency Scenarios and Response
Emergency scenarios require quick‚ effective actions to ensure safety and minimize harm. Proper training in first aid‚ CPR‚ and AED use is crucial for timely intervention and positive outcomes.
Cardiac Arrest and Choking Incidents
Cardiac arrest occurs when the heart stops functioning‚ requiring immediate CPR and AED use. Recognize symptoms like unresponsiveness and lack of breathing. For choking‚ dislodging the airway obstruction is critical. Perform back blows for mild cases and abdominal thrusts for severe blockages. Training ensures swift‚ effective responses to these life-threatening emergencies‚ improving survival chances significantly through proper techniques and timely intervention.
Response to Other Common Emergencies
Effective first aid requires quick action in various scenarios‚ such as severe bleeding‚ burns‚ fractures‚ or allergic reactions. Control bleeding with direct pressure‚ cool burns to reduce tissue damage‚ and immobilize fractures to prevent further injury. For allergic reactions‚ administer epinephrine if trained. Stay calm‚ assess the situation‚ and provide care until professional help arrives‚ ensuring the best possible outcomes in critical moments.
Legal Considerations in First Aid
Understanding legal aspects is crucial for first aid providers to protect both the victim and themselves. Knowledge of Good Samaritan Laws and documentation requirements ensures responsible and lawful care.
Good Samaritan Laws
Good Samaritan Laws protect individuals who provide first aid in good faith‚ shielding them from legal liability unless gross negligence occurs. These laws encourage bystanders to assist without fear of repercussions‚ promoting timely and compassionate care. Understanding these protections is essential for first aid providers to act confidently and responsibly in emergency situations. Always familiarize yourself with local laws to ensure compliance and awareness of your legal standing.
Documentation and Reporting Requirements
Accurate documentation is crucial after providing first aid. Records should include the incident details‚ care provided‚ and the victim’s condition. Reporting requirements vary by jurisdiction but often involve informing supervisors or authorities‚ especially in workplace incidents. Timely and detailed documentation helps in legal compliance‚ insurance claims‚ and continuous improvement of emergency response protocols. Always maintain confidentiality and adhere to local regulations when documenting and reporting incidents.
Mastering first aid‚ CPR‚ and AED skills empowers individuals to save lives. Stay updated with guidelines‚ practice regularly‚ and seek additional resources for continuous learning and preparedness.
Reinforcing Learning and Skill Retention
Regular practice and continuous learning are key to retaining first aid‚ CPR‚ and AED skills. The manual’s structured format‚ with practical exercises and visual aids‚ enhances understanding. Real-life scenarios and hands-on training reinforce muscle memory and confidence. Participants are encouraged to revisit the material periodically and use complementary resources‚ such as mobile apps‚ to stay updated and proficient in emergency response techniques.
Staying Updated with the Latest Guidelines
Staying informed about updates in first aid‚ CPR‚ and AED protocols is crucial for effective emergency response. The manual aligns with the latest guidelines from authoritative sources like the American Red Cross and ILCOR. Participants are encouraged to periodically review updates‚ attend refresher courses‚ and utilize online resources to ensure their skills remain current and aligned with best practices in emergency care.

